Is it ok to walk around barefoot in my home? I’m concerned about my feet absorbing mycotoxins.
Is it ok to walk around barefoot in my home? I’m concerned about my feet absorbing mycotoxins.
Often we end up researching and writing articles in response to client questions, and this is one such article. If your floors are warm or carpeted, it often feels good to walk around barefoot in the house. However, this may or may not be a good idea, depending on what is on your floors. Can toxins really go into or out of your feet?
“Foot detoxing” pads, baths and creams have been popular for a while. Usually they show the pad or water turning brown with “toxins” after supposedly releasing them from your body through the feet. However, there have been very few studies on their effectiveness. In a small 2012 study, the researchers sampled water from before and after foot baths with the popular IonCleanse device, as well as hair and urine samples. They found no evidence to suggest that ionic footbaths help promote the elimination of toxic elements from the body through the feet, urine, or hair. So, it’s unlikely that these methods are able to pull toxins out of the body.
However, some molecules can be absorbed through the skin (particularly the feet) into the bloodstream. You can even “taste” with your feet; if you apply garlic to the soles of your feet in a plastic bag ala this video, you can taste it in your mouth between 15 minutes to one hour later. This is because small, light molecules like allicin (the chemical released in freshly-cut garlic) can penetrate the skin and the bloodstream, traveling throughout your body. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is a chemical that has similarities to allicin and is very easily absorbed through the skin. Part of the DMSO is transformed to the volatile metabolite dimethyl sulfide, which gives a characteristic garlic- or oyster-like smell when excreted through the lungs. (Adverse reactions of dimethyl sulfoxide in humans: a systematic review) Therefore, we are susceptible to chemicals that behave in this way. Scientists and drug-researchers are constantly in search of chemicals that can deliver drugs more easily to the bloodstream, and therefore new “carriers” are of great interest.
What about mycotoxins that may happen to be on the floors? Can we get mycotoxin poisoning from walking around barefoot? Although there’s no direct answer via testing, research on individual mycotoxins shows that they can be absorbed through the skin, so it’s reasonable to assume that they can be absorbed through the skin of the soles of the feet. Since mycotoxin concentration on surfaces is highly variable, however, it remains to be seen whether concentrations sufficient to cause illness are present on floors.
We found that a 2014 paper summarizing previous research on the absorption of the most common mycotoxins through skin and their effects, was most helpful. This research documented mostly animal trials to determine toxicity, but there are also reports of workers who were accidentally exposed to these toxins. The actual methods of damage incurred by these toxins can be quite complex, so we will spare you the details, but many of them cause oxidative stress that stimulate the immune system, triggering inflammation and cell damage. Here are some examples:
- T-2 toxin, a member of the trichothecene mycotoxin family, is produced by various species of Fusarium fungus, which can infect corn, wheat, barley and rice crops in the field or during storage. It’s infamous for allegedly being used as a bioweapon during the military conflicts in Laos (1975-81), Kampuchea (1979-81), and Afghanistan (1979-81) to produce lethal and nonlethal casualties. (CBRNE - T-2 Mycotoxins) T-2 toxin causes oxidative stress, which releases cytokines (proteins that help control inflammation in the body) that are thought to cause the death of the outer layer of skin cells (keratinocyte apoptosis). T-2 mycotoxicosis can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, leukopenia, hemorrhaging, skin inflammation, and in severe cases, death. (T-2 Mycotoxicosis) The reported LD50 (amount which causes death in 50% of exposures) of T-2 toxin is approximately 1 mg/kg of body weight. (Medical Aspects of Chemical and Biological Warfare)
- Citrinin (CTN) is a product of several fungal species belonging to the genera Penicillium, Aspergillus and Monascus. To summarize, CTN under in vivo conditions has the ability to cause oxidative stress and ROS-mediated DNA damage in mouse skin upon topical exposure, leading to skin death.
- Patulin (PAT) is a toxic chemical naturally produced by several species of mold, especially within Aspergillus, Penicillium and Byssochlamys. A single topical application of PAT to mouse skin generates ROS, which causes DNA damage in skin cells. In small doses it causes death of the cells, but in larger doses it initiates tumor growth.
- Aflatoxins are products of several types of Aspergillus molds, with AFB1 known as the most potent teratogen (causing malformation of embryos), mutagen and hepatocarcinogen (causes liver cancer) of all aflatoxins. Like in the case of PAT, AFB1 may also cause skin tumors in mouse skin after long-term and higher-dose application.
- Ochratoxin A (OTA) is a fungal metabolite produced by Aspergillus ochraceus and Penicillium verrucosum. OTA is found in a variety of plant food products such as cereals. To summarize, a single topical exposure of OTA at the dose level of 20–80 μg/mouse (20-80 millionths of a gram, with a mouse weight of 40-45 grams, translates to 0.5-2.0 ppm) induces the production of ROS, resulting in the skin cell death. On the other hand, a single topical exposure of OTA at a dose level of 100 nmol/mouse causes significant enhancement of short-term markers of skin tumor promotion in mouse skin.
As you can see, the least effect of these mycotoxins is to cause skin cell death, but the worst effects are whole-body! They are effectively absorbed through the skin. However, is it reasonable to assume that they would be found on your floors, in a sufficient quantity to cause illness?
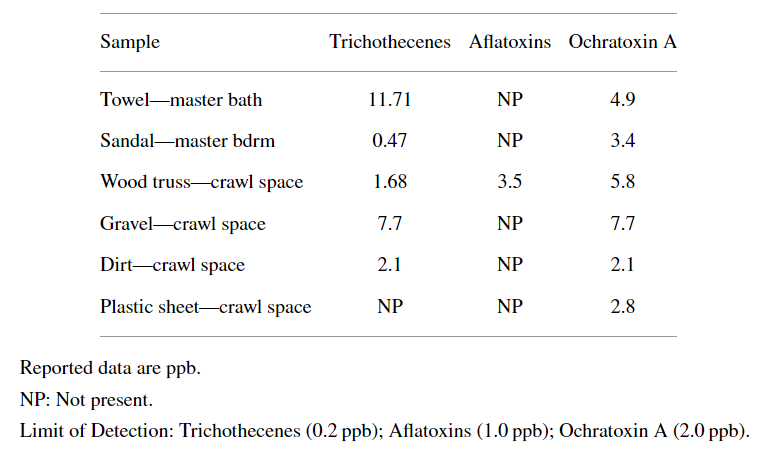
A 2012 study of a family that started to experience illness shortly after moving to a home in Hawaii in 2008 indicates that mycotoxin levels in the low parts-per-billion range on various surfaces in the home (including a sandal and a bath towel), as well as elevated fungal counts, can cause systemic illness. The father and mother, aged 40 and 39, had an 8 year old daughter, a 5 year old son and a pet dog, living in a 2-story home with a crawlspace that had water intrusion. According to one of the two inspection companies hired to investigate the home for mold, “A serious moisture/mold problem is observed in the crawlspace directly below the bedrooms. Moisture is penetrating the walls of the foundation. The HVAC system is designed to force air into the crawl space, forcing crawl space air into the bedrooms and other areas above. Moisture intrusion also results from the master shower into the crawl space as well as from sprinklers, damp soil against the foundation, lack of roof gutters, and poor grading.” Similar findings were in the second report, plus: “Smoke testing revealed communication between the crawl space and upper level bedrooms via electrical outlets and electrical ducts and plumbing. The conduit holes were not sealed, permitting observance of light coming through spaces in the floor joists. A musty odor was present in the master bathroom and noted to get stronger when the fan coil was turned on.” ERMI tests for mold indicated ERMI levels of 2 to 3 throughout the home, which “represent a moderately high index, and further investigation should be conducted to establish if your home has a mold contamination problem”. (Interpreting ERMI test results) Here are the test results for mycotoxins; mycotoxins can be measured from air or dust samples and in this case the dust was analyzed:All four of the family members and the dog tested positive for OTA and some for tricothecenes in their urine; they had health problems involving the upper and lower respiratory tract, headaches, neurocognitive deficits, and severe sinusitis. They had chronic sinusitis and nasal inflammation, and the isolation of bacteria (Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter) and molds (Penicillium and Aspergillus) from nasal secretions from the father and daughter is consistent with other cause and effect symptoms of mold exposure. Even the dog suffered from 72 lesions, an ear mass and lipomas (which were surgically removed), in were found OTA and tricothecenes. The mother gave birth to a daughter 3 months after moving out of the home, which had skin inflammation and discolorations because of being exposed to mycotoxins in the womb and via breastmilk.
Therefore, we can conclude from this sad scenario that mold, bacteria and mycotoxins are a real concern in house dust when the home has water intrusion and mold issues. There’s no way to know how much of the mycotoxins were inhaled versus absorbed through their skin, but of course young children are closer to the floor, often crawling and sitting on it, thus sitting in dust, stirring up dust, and breathing it in. The dog obviously suffered from laying on the floor!
According to IndoorScience, a reputable indoor air-quality testing company,
there are no guidelines for “acceptable” amounts of mycotoxins in house dust,
mycotoxin testing is much more expensive than standard mold testing, and
there are only a few labs that perform mycotoxin testing.
However, if you have water intrusion or mold problems in your home that you suspect are causing health problems, mycotoxins or toxins from actinobacteria (see our article here) could very well be the culprit. In these cases, solving the water intrusion problem and remediation and thorough cleaning will also remove the mycotoxins and bacterial toxins! Here are some tips for maintaining a cleaner home from our related article:
Invest in a HEPA air cleaner to remove dust from the air
Clean floors regularly with a HEPA vacuum and mopping (some appliances do both)
Filter the air that comes into your home via window filters
Change your HVAC filter regularly and even upgrade it if possible
Try to remove your outdoor shoes at the door, and wear indoor shoes or slippers only in the home
Minimize clutter, upholstery and carpets that can hold dust.
These are also common recommendations of doctors and practitioners who see mold illness in their patients, because removing them from surfaces is helpful whether the toxins are inhaled or absorbed. If you suspect water intrusion anywhere in your home (even in places you can’t see, like the crawlspace or attic), of course you’ll need to address remediation in the moldy area pronto. However, since you don’t know how air currents may be carrying dust and toxins into the living space, it’s a safe bet to also step up the cleaning and keep your shoes on!
Photo by Jimmy Chang on Unsplash