Navigating Electromagnetic Frequency (EMF) Radiation
Navigating Electromagnetic Frequency (EMF) Radiation
Convenience and technology go hand in hand. If you want to save money at your store, the store’s “app” gives you the deals straight to your cellphone. Smart doorbells and smart thermostats keep us safe and comfortable. Baby monitors and cameras help us to keep an eye on the kids. What could be better than knowing and doing more than your parents ever could?
The only problem with these perks is the energy they emit while helping you. It’s called electromagnetic frequency radiation, or EMF for short. Now, don’t get me wrong. Anything that uses electricity, even a washing machine motor from the 1960’s, will have an electricmagnetic field associated with it, because that’s what electricity does. Electrons move inside the electric supply cord, back and forth at the rate of about 60 cycles per second (60 hertz) in the US. When the motor is energized, the electrons moving through the coils of the motor generate an electric field that spins the drum, and another motor that pumps out the water. Electricity is right up there with indoor plumbing as something we wouldn’t want to be without!
There is a big difference, however, between the way an old washing machine and a new cellphone use electricity and emit radiation. The old washing machine had two modes, on and off, and it used power straight from the wall (110-120 volts alternating current, 60 hertz) with no transformers, inverters or rectifiers involved. The cellphone, however, could never be plugged into the wall because it uses low voltage (12 volts) and “direct current” (DC). The charger is plugged into the wall to convert high AC to low DC voltage to feed it to the sensitive electronics of the phone. The phone, once charged, is essentially a battery with several different modes and the ability to radiate signals in a radius around it (about 30 feet for Bluetooth). This generates two different problems with it: the way the charger manipulates electricity (taking the AC and converting it to DC and lowering the voltage) and the way both the charger and cellphone emit radiation.
“Dirty electricity” is admittedly not easy to understand. After all, electricity is promoted to be the world’s cleanest energy, right? We are enticed to replace everything that emits carbon with newer appliances that are “greener” for the planet with “no” emissions. Yet, there is no such thing as free. There are trade-offs for every convenience and savings in the pocket don’t always mean a savings to our peace of mind or health.
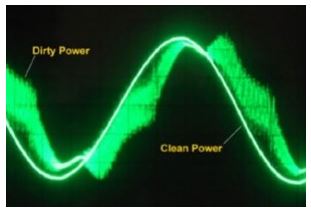
Since dirty electricity can’t be seen, smelled or touched, the best way to describe it is in pictures. The photo below is of an alternating current electrical signal. (If you don’t understand the difference between alternating and direct current, here is a really good video). The bright green line is clean power, which in alternating current is a smooth rolling sine wave (the peaks and valleys occur 60 times per minute, hence 60 hertz). The green fuzz is dirty electricity, which is made up of jagged spikes that cause more radiation and can cause damage to equipment. Where does the green fuzz come from?
Source: What is Dirty Electricity?
The green fuzz, or dirty power, is what is left over when you convert AC into DC or maneuver it in other ways. Here is a video that visualizes what the little transformer/rectifiers on your cellphone charger and laptop chargers are doing to convert the power from the wall (120 volts AC) into usable power for your device (12 volts DC). Chopping up the signal and smoothing it out causes some power “noise” and energy wastage. Have you ever felt the transformer plug of the phone, or of your laptop computer? Heat is another sign that there is energy being wasted.
The green fuzz is not just ruining a nice picture of a sine wave. The spikes and unpredictable energy can cause damage to electronics as well as to our bodies. Dirty electricity can cause the following health issues (What is Dirty Electricity?) :
- Headaches
- Sleep Disturbances
- Fatigue
- Tinnitus
- Cognitive Impairment
- Heart Arrhythmia
- Mood Swings
- Weakening of the nervous, endocrine and immune systems
- Increased risk of serious chronic illnesses such as cancer
Why does dirty electricity affect us? Because we, as humans, run on electricity too. The nervous system that regulates many functions in our bodies is electrical, and its sensitive equipment and signals can be affected by outside electromagnetic radiation. For example, scientists have known for a while that some types of EMF radiation can actually cause bone to grow, and calcium channel blockers (which are frequently prescribed for heart arrhythmias) block EMF effects because they block electrical activity in the body. (Electromagnetic fields act via activation of voltage-gated calcium channels to produce beneficial or adverse effects)
Many health effects are only manifested when a major change occurs, like the installation of a smart meter on our home, or a newly installed cellphone tower coming online nearby, or moving into an apartment with wi-fi signals surrounding yours. However, symptoms can also be gradual as well. Like the effects of mold and mycotoxins, EMF radiation seems to affect those who are most sensitive to them. When most of the population are not affected outwardly, regulation of new and more profuse radiation is not a priority. However, quantified effects on our microbiology such as blood, organs and DNA through research should be enough to increase awareness of its dangers.
Although governments and health organizations (including the WHO) have denied that there is any risk to our health from dirty electricity, here is a short list of studies that have shown there is a cause and effect. Since animals are even more sensitive than humans (termed “canaries”), included are a couple of real-world case studies on how EMF has affected farm animals, with detrimental effects on their behavior, output and reproduction.
- Electromagnetic hypersensitivity: biological effects of dirty electricity with emphasis on diabetes and multiple sclerosis
- Power quality affects teacher wellbeing and student behavior in three Minnesota Schools
- Microwave frequency electromagnetic fields (EMFs) produce widespread neuropsychiatric effects including depression
- Low Intensity Electromagnetic Fields Act via Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel (VGCC) Activation to Cause Very Early Onset Alzheimer's Disease: 18 Distinct Types of Evidence.
- Wi-Fi is an important threat to human health
- Conspicuous behavioural abnormalities in a dairy cow herd near a TV and radio transmitting antenna
- Report to Michigan Oversight Committee regarding effects of stray voltage on dairy cattle
The good news is that you can take control in your own home and eliminate some causes of dirty electricity. Dimmer switches and compact fluorescent bulbs (CFLs) are some of the worst offenders, so try to eliminate these in your home. Unplug computer and cellphone chargers whenever they are not in use, and when they are in use, keep them as far from you as possible. Special paints, coverings and cases can help to shield you from harmful EMF--you can check out these types of shields here.
Other sources of EMF radiation can be controlled as well:
- Smart meters: Smart meters are power meters that broadcast a signal similar to your cellphone, to the electric company so that they can monitor power usage remotely. Although many utility companies claim that their meters only “broadcast” less than a minute per day, the pulses sent by the meter (typically 3 milliseconds each) can be over 10,000 times per day. (Frequently Asked Questions about Smart Meters) If you can, opt out of having a smart meter placed on your building and have it replaced with an analog meter. If you cannot, there are meter cages available that can significantly block EMF radiation from the meter. This video shows how high and frequently EMF radiation can be emitted from Smart Meters.
- Wireless routers: Unplug wireless routers at night and place them away from bedrooms or areas where people spend extended periods of time.
- Baby Monitors: Research the baby monitor you use to see whether it is safe, and place it a safe distance from the crib or bed.
- Cellphones: Restrict cellphone use by children and for adults, opt to use headsets or speakerphone as often as possible, carrying the phone in a purse or away from your body.
- Solar power inverters: the process of converting low-voltage direct current into high voltage alternating current produces dirty electricity, which can build up over time to dangerous levels inside your home.
There are two types of devices that can detect EMF radiation: a Graham-Stetzer meter that measures dirty electricity in GS units (I’ll discuss this next), OR simply an AM radio! AM radios can pick up low-order harmonics. Tune it down to the lowest amplitude, about 500 kHz, to start, and turn up the volume a bit to hear the static. Bring it near a possible EMF emitter like a cellphone or its charger plug, and listen for an increase in static or “ticks” to indicate it is emitting EMF radiation. You can also tune the amplitude up to its highest, to about 1600 kHz, to see what’s going on there. (This setting is better for “hearing” the EMF from your cellphone, which typically broadcasts on even higher frequencies). This video shows how to use an AM radio inside your home to detect relative volumes of EMF radiation from different appliances (the dimmer switch really puts out a lot)! Another video shows you how to detect whether EMF radiation is coming from the line power (from the power company), or from the devices, like lighting and electronics, in your house.
If you find you have a lot of EMF radiation with the AM radio, then you might want to invest in a more quantitative meter that shows the real levels of radiation. With a meter designed to detect EMF radiation, you can walk around your home to measure these levels. The original meter, called a Graham-Stetzer Microsurge meter (after its inventors) measures EMF radiation in units of “GS”. According to Dave Stetzer, a GS unit is a measure of the energy on electrical wires generated by high frequency transients and harmonics, and is influenced by voltage, amplitude and frequency. (presentation by Dr. Magda Havas, PhD). According to one electrician, under 200 GS is good and acceptable, but Dr. Havas has noted that those who are more sensitive and already have health issues like diabetics and multiple sclerosis patients, require readings under 40 GS. In order to reduce EMF, a “Stetzerizer filter” can simply be plugged into any normal electrical outlet. This video shows how to use a Graham-Stetzer meter and Stetzerizer filters to get rid of dirty electricity. After removing as many offending appliances as possible like dimmer switches, CFL bulbs and unused electronic charges, the filters are very easy to use–just plug them in!
If you have unexplained or chronic health issues, it’s worth exploring and measuring EMF radiation in your home. This type of pollution can’t be seen, smelled or heard but the health effects on many people are debilitating, and intervention can provide significant relief. We hope you will do your own research on EMF radiation!
Photo by Andreas Haslinger on Unsplash